Spring思维导图,让Spring不再难懂(mvc篇)
写在前面
生活就像海洋,只有意志坚强的人才能到达彼岸。
已经很久没有发文章了呀,想必大家都挂念我了,哈哈。
温故而知新,今天一起来复习一下spring mvc的内容吧。
spring mvc简介与运行原理
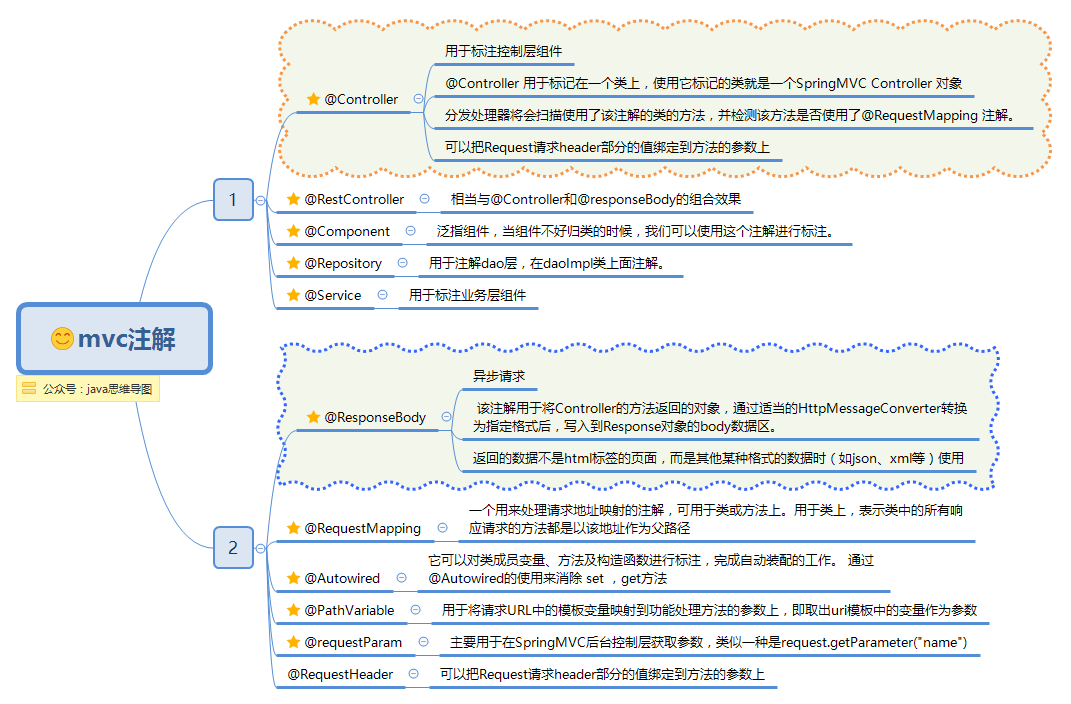
Spring的模型-视图-控制器(MVC)框架是围绕一个DispatcherServlet来设计的,这个Servlet会把请求分发给各个处理器,并支持可配置的处理器映射、视图渲染、本地化、时区与主题渲染等,甚至还能支持文件上传。
原理.png
- (1) Http请求:客户端请求提交到DispatcherServlet。
- (2) 寻找处理器:由DispatcherServlet控制器查询一个或多个HandlerMapping,找到处理请求的Controller。
- (3) 调用处理器:DispatcherServlet将请求提交到Controller。
- (4)(5)调用业务处理和返回结果:Controller调用业务逻辑处理后,返回ModelAndView。
- (6)(7)处理视图映射并返回模型: DispatcherServlet查询一个或多个ViewResoler视图解析器,找到ModelAndView指定的视图。
- (8) Http响应:视图负责将结果显示到客户端。
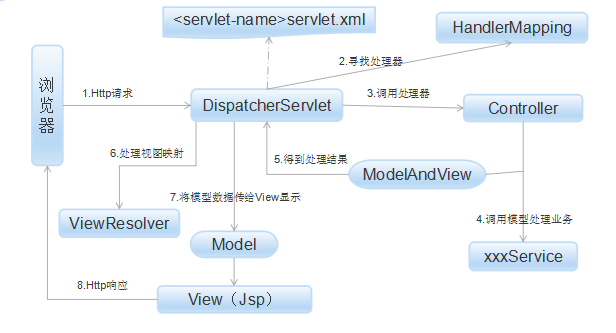
主要注解
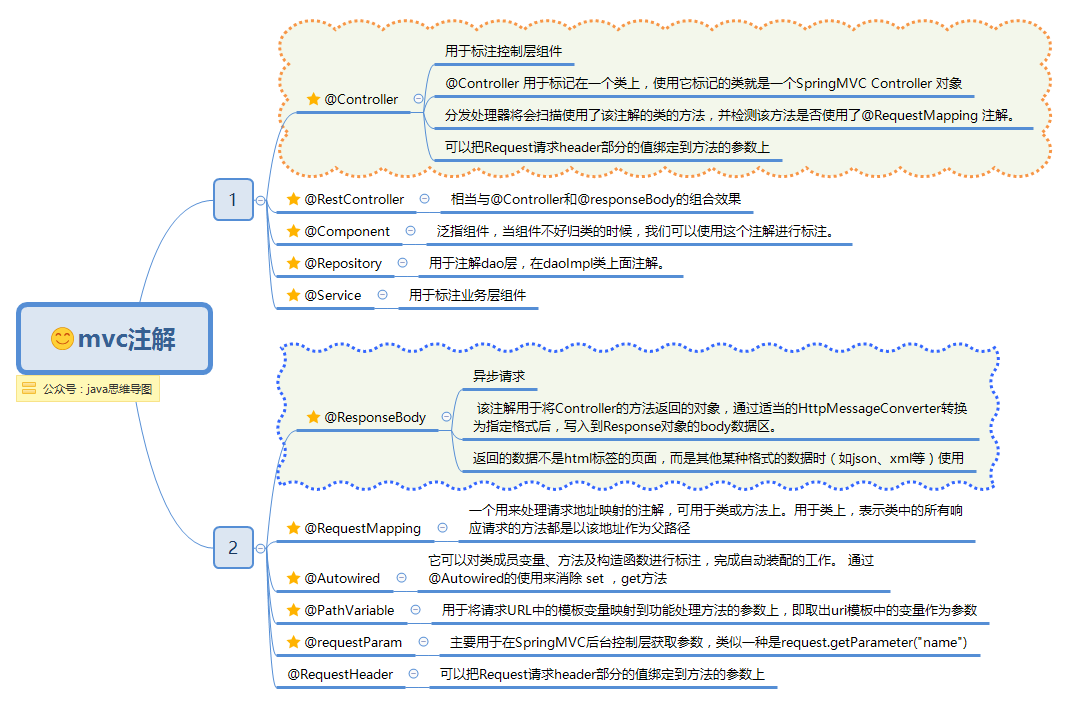
spring mvc注解.png
ContextLoaderListener
在讲ContextLoaderListener之前,首先来了解一下web.xml的作用。
- 一个web中可以没有web.xml文件,也就是说,web.xml文件并不是web工程必须的。web.xml文件是用来初始化配置信息:比如Welcome页面、servlet、servlet-mapping、filter、listener、启动加载级别等。当你的web工程没用到这些时,你可以不用web.xml文件来配置你的Application。
- 当要启动某个web项目时,服务器软件或容器如(tomcat)会第一步加载项目中的web.xml文件,通过其中的各种配置来启动项目,只有其中配置的各项均无误时,项目才能正确启动。web.xml有多项标签,在其加载的过程中顺序依次为:context-param >> listener >> fileter >> servlet。(同类多个节点以出现顺序依次加载)
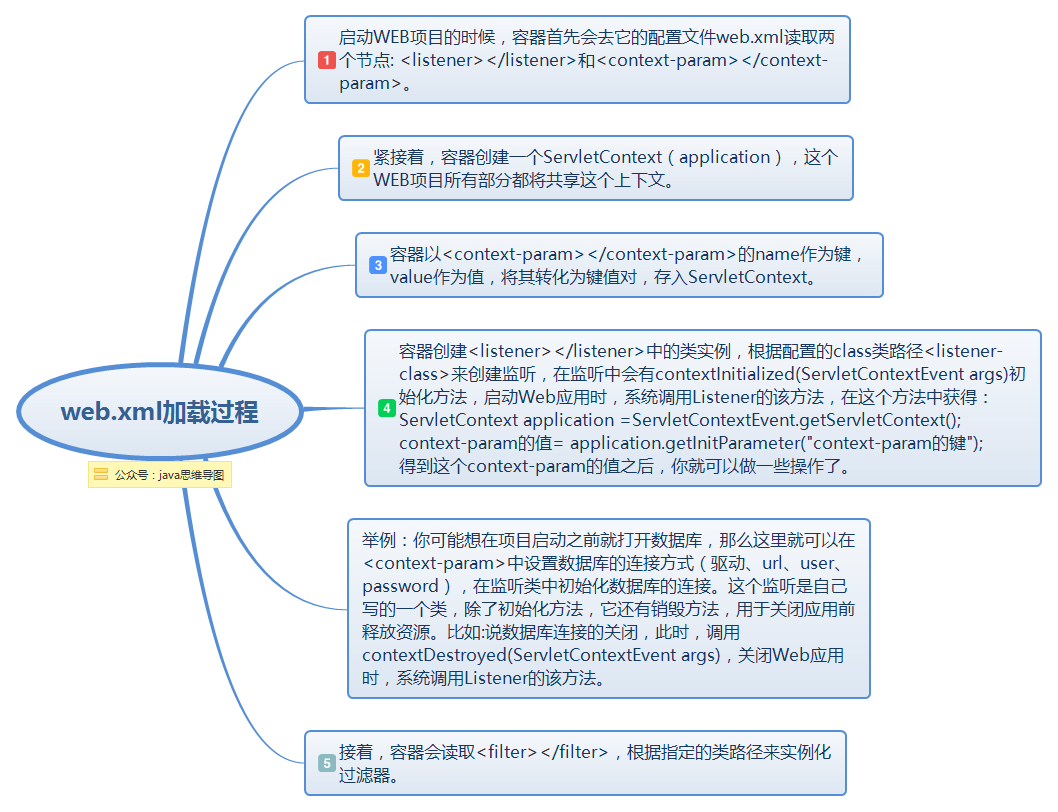
web.xml加载过程.png
而spring mvc启动过程大致分为两个过程:
- ContextLoaderListener初始化,实例化IoC容器,并将此容器实例注册到ServletContext中。
- DispatcherServlet初始化。
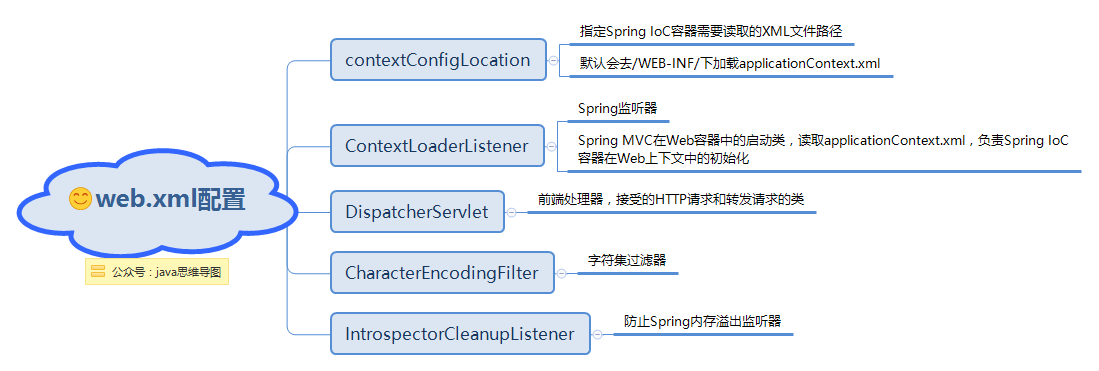
web.xml配置.png
其中ContextLoaderListener监听器它实现了ServletContextListener这个接口,在web.xml配置这个监听器,启动容器时,就会默认执行它实现的方法。在ContextLoaderListener中关联了ContextLoader这个类,所以整个加载配置过程由ContextLoader来完成。
- ContextLoaderListener在web.xml中的配置
contextConfigLocation
/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
ServletContextListener 接口有两个方法:contextInitialized,contextDestroyed
DispatcherServlet
Spring MVC框架,与其他很多web的MVC框架一样:请求驱动;所有设计都围绕着一个中央Servlet来展开,它负责把所有请求分发到控制器;同时提供其他web应用开发所需要的功能。不过Spring的中央处理器,DispatcherServlet,能做的比这更多。
下图展示了Spring Web MVC的DispatcherServlet处理请求的工作流。熟悉设计模式的朋友会发现,DispatcherServlet应用的其实就是一个“前端控制器”的设计模式(其他很多优秀的web框架也都使用了这个设计模式)。
- 流程图
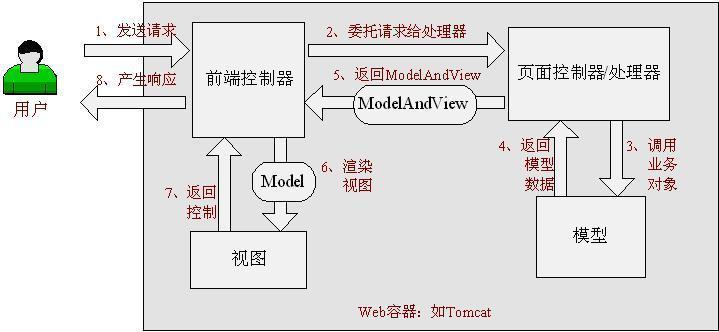
spring mvc处理请求的流程.jpg
- 在web.xml中的配置
dispatcher
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
1
dispatcher
/
其中
- load-on-startup:表示启动容器时初始化该Servlet;
- url-pattern:表示哪些请求交给Spring Web MVC处理, “/” 是用来定义默认servlet映射的。也可以如“*.html”表示拦截所有以html为扩展名的请求。
在Spring MVC中,每个DispatcherServlet都持有一个自己的上下文对象WebApplicationContext,它又继承了根(root)WebApplicationContext对象中已经定义的所有bean。这些继承的bean可以在具体的Servlet实例中被重载,在每个Servlet实例中你也可以定义其scope下的新bean。
WebApplicationContext继承自ApplicationContext,它提供了一些web应用经常需要用到的特性。它与普通的ApplicationContext不同的地方在于,它支持主题的解析,并且知道它关联到的是哪个servlet(它持有一个该ServletContext的引用)
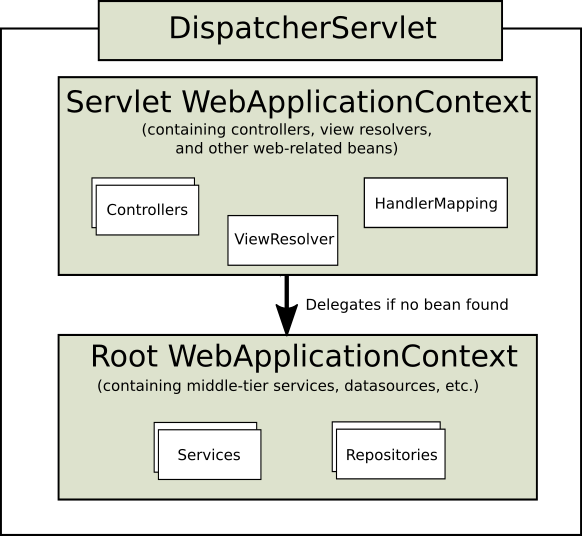
DispatcherServlet继承结构
spring mvc同时提供了很多特殊的注解,用于处理请求和渲染视图等。DispatcherServlet初始化的过程中会默认使用这些特殊bean进行配置。如果你想指定使用哪个特定的bean,你可以在web应用上下文WebApplicationContext中简单地配置它们。
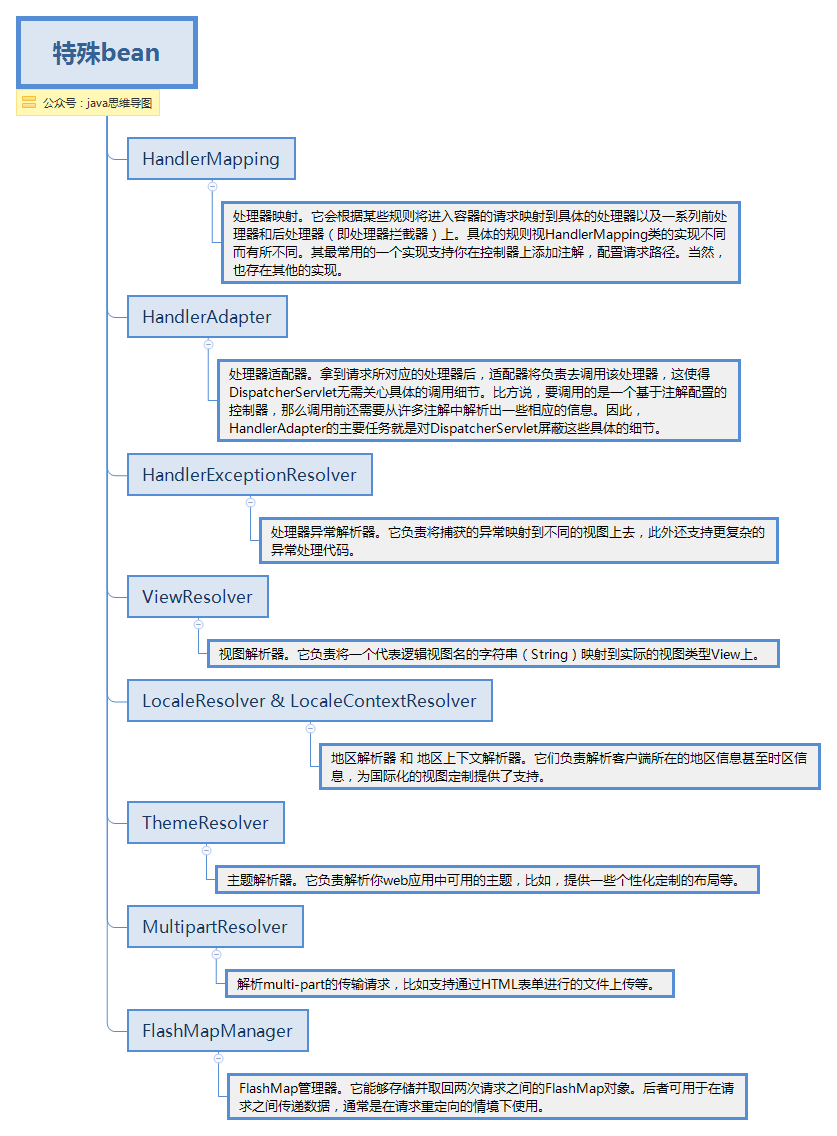
特殊bean.png
其中,常用的ViewResolver的配置。以jsp作为视图为例
配置上传文件限制MultipartResolver
applicationContext.xml中的标签
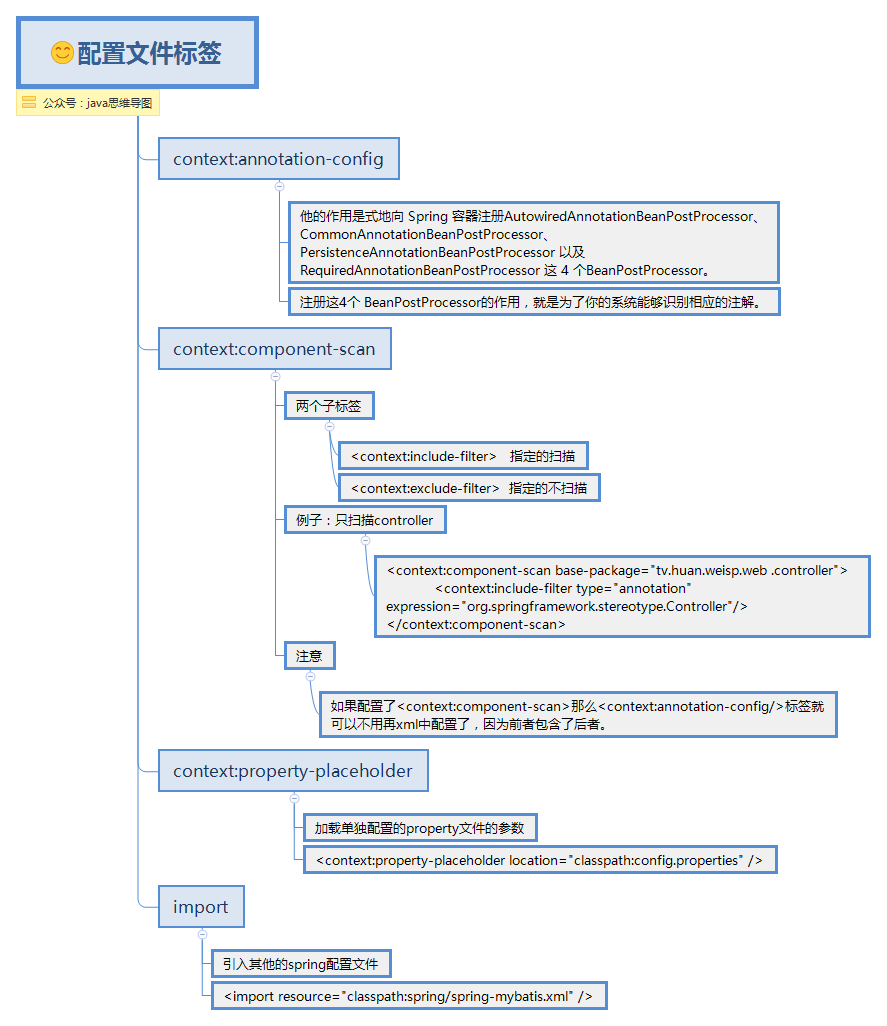
applicationContext.xml配置文件标签.png
文件上传
前面说到DispatcherServlet中有个特殊的Bean叫MultipartResolver,可用于限制文件的上传大小等。当解析器MultipartResolver完成处理时,请求便会像其他请求一样被正常流程处理。
- 表单
- 控制器
@RequestMapping(path = "/form", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String handleFormUpload(@RequestParam("name") String name, @RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file) {
if (!file.isEmpty()) {
byte[] bytes = file.getBytes();
// store the bytes somewhere
return "redirect:uploadSuccess";
}
return "redirect:uploadFailure";
}
异常处理
先来说下常见的异常处理有几种方式,如下图:
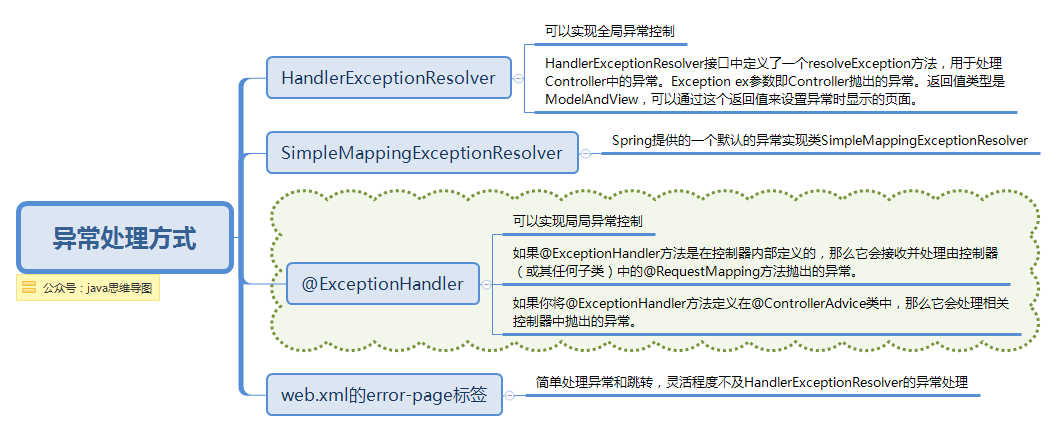
异常处理方式.png
Spring的处理器异常解析器HandlerExceptionResolver接口的实现负责处理各类控制器执行过程中出现的异常。也是上面提到的,是DispatcherServlet中的特殊bean,可以自定义配置处理。
某种程度上讲,HandlerExceptionResolver与你在web应用描述符web.xml文件中能定义的异常映射(exception mapping)很相像,不过它比后者提供了更灵活的方式。比如它能提供异常被抛出时正在执行的是哪个处理器这样的信息。
- HandlerExceptionResolver 提供resolveException接口
public interface HandlerExceptionResolver {
ModelAndView resolveException(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex);
}
- 在BaseController中使用 @ExceptionHandler注解处理异常
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public Object exceptionHandler(Exception ex, HttpServletResponse response, HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {
String url = "";
String msg = ex.getMessage();
Object resultModel = null;
try {
if (ex.getClass() == HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException.class) {
url = "admin/common/500";
System.out.println("--------毛有找到对应方法---------");
} else if (ex.getClass() == ParameterException.class) {//自定义的异常
} else if (ex.getClass() == UnauthorizedException.class) {
url = "admin/common/unauth";
System.out.println("--------毛有权限---------");
}
String header = req.getHeader("X-Requested-With");
boolean isAjax = "XMLHttpRequest".equalsIgnoreCase(header);
String method = req.getMethod();
boolean isPost = "POST".equalsIgnoreCase(method);
if (isAjax || isPost) {
return Message.error(msg);
} else {
ModelAndView view = new ModelAndView(url);
view.addObject("error", msg);
view.addObject("class", ex.getClass());
view.addObject("method", request.getRequestURI());
return view;
}
} catch (Exception exception) {
logger.error(exception.getMessage(), exception);
return resultModel;
} finally {
logger.error(msg, ex);
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
- *在web.xml中处理异常 *
403
/403.html
404
/404.html
500
/500.html
- 来一个问题:HandlerExceptionResolver和web.xml中配置的error-page会有冲突吗?
解答:如果resolveException返回了ModelAndView,会优先根据返回值中的页面来显示。不过,resolveException可以返回null,此时则展示web.xml中的error-page的500状态码配置的页面。
当web.xml中有相应的error-page配置,则可以在实现resolveException方法时返回null。
API文档中对返回值的解释:
** return a corresponding ModelAndView to forward to, or null for default processing.**